简易客户端-服务端
服务端
创建一个ServerSocket实例, 绑定对应的端口之后, 在while循环中阻塞等待客户端的请求, 客户端请求成功之后,创建一个输入流和一个输出流 再进行数据交互.
- 创建一个ServerSocket并绑定端口
- 阻塞等待客户端请求
- 链接之后, 交互数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
final String QUIET = "quiet";
ServerSocket server = null;
try {
server = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT);
System.out.println("[启动服务器, 监听端口 " + DEFAULT_PORT
+ "]");
while (true) {
// 等待链接
Socket client = server.accept();
System.out.println("[客户端 " +
client.getPort() + " 已经链接]");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(client.getOutputStream()));
// 读取客户端数据
String msg = null;
while (((msg = reader.readLine()) != null)) {
System.out.println("[客户端 " + client.getPort() + "发送数据 " + msg + "]");
// 返回个客户端数据
writer.write("{ echo " + msg + "} \n");
writer.flush();
if(QUIET.equalsIgnoreCase(msg)){
break;
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (server != null) {
try {
server.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端
创建一个Socket实例(服务器地址, 端口), 之后将创建两个输入流(一个用于读取服务端发送的数据, 一个用于读取用户输入的数据), 一个输出流(将用户输入的数据发送个服务端)
- 创建Socket
- 链接服务器
- 和服务器交互
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST = "localhost";
final String QUIET = "quiet";
final int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 8888;
try (
Socket client = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST, DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT);
// 创建IO流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(client.getOutputStream()));
// 等待用户输入信息
BufferedReader consoleReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
) {
while (true) {
// 读取用户输入数据
String input = consoleReader.readLine();
// 发送给服务器
writer.write(input + "\n");
writer.flush();
// 输出服务器返回数据
String accept = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("[服务器 发送数据 " + accept + "]");
// 查看是否退出
if(QUIET.equalsIgnoreCase(input)){
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
总结
上述一个简单的聊天室程序完成,但是因为
- server.accept()
- InputStream.read()
- OutputStream.write()
均存在阻塞问题, 当有新的客户端发起请求时,服务端需要执行完上一个请求之后,才能去执行这个请求.所有我们可以将阻塞的部分独立出来用一个新的线程执行这部分内容.
- 将用户的输入处理用一个新的线程处理
- 将服务端中的数据处理独立出来, 创建一个对应的线程来执行对应客户端的数据交互
优化1: 服务端为每个请求创建线程处理
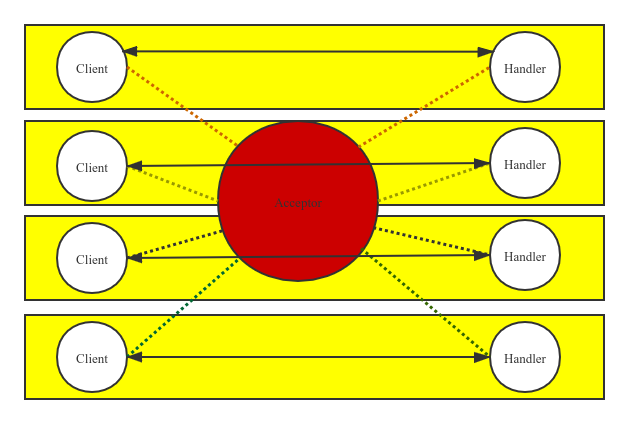
服务端
Constant
用于存放一些静态常量
public interface Constant {
/**
* 默认端口
*/
int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
/**
* IP地址
*/
String DEFAULT_HOST = "localhost";
/**
* 退出命令
*/
String QUIT = "quit";
}
Server
和基础的版本有所不同的是, 服务端转发消息给客户端,是除了发送消息的那个客户端.
public class ChatServer implements Constant {
private ServerSocket server = null;
private ExecutorService executor;
private Map<Integer, Writer> connectionClients;
public ChatServer() {
this.connectionClients = new HashMap<>();
this.executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
}
// 新增用户添加到map
public synchronized void add(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket != null) {
int port = socket.getPort();
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
connectionClients.put(port, writer);
System.out.println("客户端 [" + port + "] 已经连接服务器");
}
}
// 下线客户移除
public synchronized void removeClient(Socket socket) throws IOException {
if (socket != null) {
int port = socket.getPort();
if (connectionClients.containsKey(port)) {
connectionClients.get(port).close();
}
connectionClients.remove(port);
System.out.println("客户端 [" + port + "]已经断开连接");
}
}
// 转发消息
public synchronized void forwardMSG(Socket socket, String msg) throws IOException {
// 转发给除去发送者的其他在线用户
for (Integer integer : connectionClients.keySet()) {
if (!integer.equals(socket.getPort())) {
Writer writer = connectionClients.get(integer);
writer.write(msg);
writer.flush();
}
}
}
// 全部转发
public synchronized void forwardAllMSG(String msg) throws IOException {
for (Integer integer : connectionClients.keySet()) {
connectionClients.get(integer).write(msg);
connectionClients.get(integer).flush();
}
}
public synchronized void close(){
if(server != null){
try {
server.close();
System.out.println("关闭服务器");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void start() {
try {
// 绑定监听端口
server = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT);
System.out.println("[启动服务器, 监听端口 " + DEFAULT_PORT
+ "]");
while (true) {
// 等待客户端连接
Socket socket = server.accept();
// 创建新的线程, 用于处理客户端数据
new Thread(new ChatHandler(socket, this)).start();
//executor.execute(new ChatHandler(socket, this));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer server = new ChatServer();
server.start();
}
}
ChatHandler
用于处理和客户端交互的线程
public class ChatHandler implements Runnable, Constant {
Socket client;
ChatServer chatServer;
public ChatHandler(Socket socket, ChatServer chatServer){
this.client = socket;
this.chatServer = chatServer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 存储新上线用户
chatServer.add(client);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
String msg = null;
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null){
// 读入客户端的消息
String fwdMSG = "客户端 [" + client.getPort() + "] 消息为 " + msg + "\n";
System.out.print(fwdMSG);
// 读出转发给其他的客户端
chatServer.forwardMSG(client, fwdMSG);
// 检测是否退出
if(QUIT.equalsIgnoreCase(msg)){
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
chatServer.removeClient(client);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端
除了将数据发送给服务端以及接受服务端的数据,还需要一个接受用户产生的数据的线程
Client
public class ChatClient implements Constant {
private Socket socket;
private BufferedReader reader;
private BufferedWriter writer;
// 发送给服务器数据
public void send(String msg) throws IOException {
if (!socket.isOutputShutdown()) {
writer.write(msg + "\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
// 接受服务器转发的信息
public String receive() throws IOException {
String msg = null;
if (!socket.isInputShutdown()) {
msg = reader.readLine();
}
return msg;
}
// 关闭
public void close() {
if (writer != null) {
try {
System.out.println("客户端" + socket.getLocalPort() + "关闭");
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 准备退出
public boolean readyQuit(String s) {
return s.equalsIgnoreCase(QUIT);
}
// 开始
public void start() {
try {
socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_HOST, DEFAULT_PORT);
writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
// 等待用户输入信息
new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start();
// 读取服务器数据
String msg = null;
while ((msg = receive()) != null){
System.out.println(msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient();
chatClient.start();
}
}
UserInputHandler
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable, Constant {
ChatClient chatClient;
public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient) {
this.chatClient = chatClient;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 等待用户输入
BufferedReader consoleReader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) {
// 获取用户输入数据
String input = consoleReader.readLine();
// 向服务器发送输入数据
chatClient.send(input);
if(chatClient.readyQuit(input)){
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
总结
该模型最大的问题就是缺乏弹性伸缩能力,当客户端并发访问量增加后,服务端的线程个数和客户端并发访问数呈1:1的正比关系,Java中的线程也是比较宝贵的系统资源,线程数量快速膨胀后,系统的性能将急剧下降,随着访问量的继续增大,系统最终就死掉了。
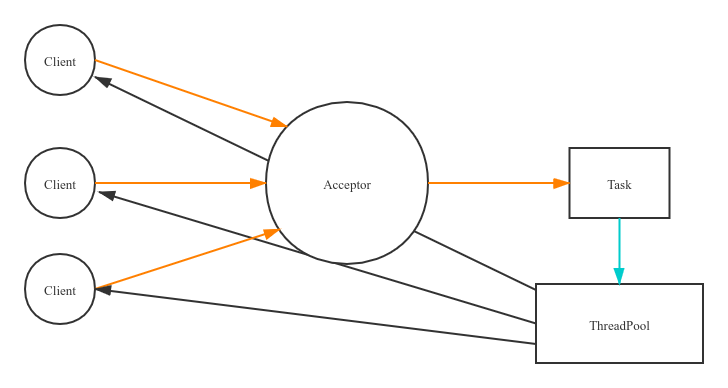
优化2: 服务端使用线程池来处理客户端的请求
为了改进这种一连接一线程的模型,我们可以使用线程池来管理这些线程,实现一个或多个线程处理多个客户端请求的模型(服务端的线程个数和客户端并发访问数呈M:N的关系,N可以远远大于M,但是底层还是使用的同步阻塞I/O),通常被称为“伪异步I/O模型“。
伪异步I/O模型图:
和优化1绝大多数部分的代码是类似的,所以只展示服务端需要修改的部分
private ExecutorService executor;
public void start() {
try {
// 绑定监听端口
server = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT);
System.out.println("[启动服务器, 监听端口 " + DEFAULT_PORT
+ "]");
while (true) {
// 等待客户端连接
Socket socket = server.accept();
// 创建新的线程, 用于处理客户端数据
new Thread(new ChatHandler(socket, this)).start();
executor.execute(new ChatHandler(socket, this));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close();
}
}
优化3: NIO
服务端
public class ChatServer implements NioConstant {
private ServerSocketChannel server;
private Selector selector;
// 读取 buffer
private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
// 写入 buffer
private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
// 自定义端口
private int port;
public ChatServer(){
this(DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public ChatServer(int port){
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
try {
// 打开一个ServerSocket 的 Channel
server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞
server.configureBlocking(false);
// 得到一个关于该ServerSocketChannel的ServerSocket、并且绑定端口
server.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 打开Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// 把ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector , 设置监听事件为ACCEPT
server.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("启动服务器,监听端口:"+ port +"...");
while(true){
// 本身是阻塞式调用
selector.select();
// 触发事件集
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for(SelectionKey key : selectionKeys){
// 处理被触发的事件
handles(key);
}
// 处理完成后,手动清空
selectionKeys.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
close(selector);
}
}
private boolean readyToQuit(String msg){
return QUIT.equalsIgnoreCase(msg);
}
private synchronized void close(Closeable closeable){
if(closeable != null){
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private String receive(SocketChannel client) throws IOException {
// 写模式
rBuffer.clear();
while((client.read(rBuffer)) > 0);
// 读模式
rBuffer.flip();
return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer));
}
private void forwardMessage(SocketChannel client , String fwdMsg) throws IOException {
for(SelectionKey key : selector.keys()){
Channel connectedClient = key.channel();
if(connectedClient instanceof ServerSocketChannel){
continue;
}
if(key.isValid() && !client.equals(connectedClient)){
// 写模式
wBuffer.clear();
wBuffer.put(charset.encode(getClientName(client) +":"+fwdMsg));
// 读模式
wBuffer.flip();
while(wBuffer.hasRemaining()){
((SocketChannel) connectedClient).write(wBuffer);
}
}
}
}
private String getClientName(SocketChannel client){
return "客户端["+client.socket().getPort()+"]";
}
private void handles(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// ACCEPT事件 - 和客户端建立了连接
if(key.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel client = server.accept();
// 设置成非阻塞
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(getClientName(client)+"已连接");
}
// READ事件 - 客户端发送了消息
else if(key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
String fwdMsg = receive(client);
if(fwdMsg.isEmpty()){
// 客户端异常 , 不再监听这个事件
key.cancel();
// 更新监听事件状态
selector.wakeup();
} else{
forwardMessage(client , fwdMsg);
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if(readyToQuit(fwdMsg)){
key.cancel();
selector.wakeup();
System.out.println(getClientName(client)+"已断开");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatServer server = new ChatServer();
server.start();
}
}
客户端
public class ChatClient implements NioConstant {
private String host;
private int port;
private SocketChannel client;
private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
private Selector selector;
private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public ChatClient(){
this(DEFAULT_HOST , DEFAULT_PORT);
}
public ChatClient(String host , int port){
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
// 检查用户是否准备退出
public boolean readyQuit(String msg){
return QUIT.equalsIgnoreCase(msg);
}
public void close(Closeable closeable){
if(closeable != null){
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void start(){
try {
selector = Selector.open();
client = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞
client.configureBlocking(false);
client.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host , port));
while(true){
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
for(SelectionKey key : selectionKeys){
handles(key);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClosedSelectorException e){
// 用户正常退出,产生的异常
} finally {
close(selector);
}
}
private void handles(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// CONNECT事件 - 连接就绪事件
if(key.isConnectable()){
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if(client.isConnectionPending()){
client.finishConnect();
// 处理用户的输入
new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start();
}
client.register(selector , SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// READ事件 - 服务器转发消息
else if(key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
String msg = receive(client);
if(msg.isEmpty()){
// 服务器异常
close(selector);
}
else{
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
private String receive(SocketChannel client) throws IOException {
// 写模式
rBuffer.clear();
while(client.read(rBuffer) > 0);
// 写模式
rBuffer.flip();
return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer));
}
public void send(String msg) throws IOException {
if(msg.isEmpty()){
return ;
}
// 写模式
wBuffer.clear();
wBuffer.put(charset.encode(msg));
wBuffer.flip();
while(wBuffer.hasRemaining()){
client.write(wBuffer);
}
// 检查用户是否准备退出
if(readyQuit(msg)){
close(selector);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatClient client = new ChatClient();
client.start();
}
}