Vector源码解读
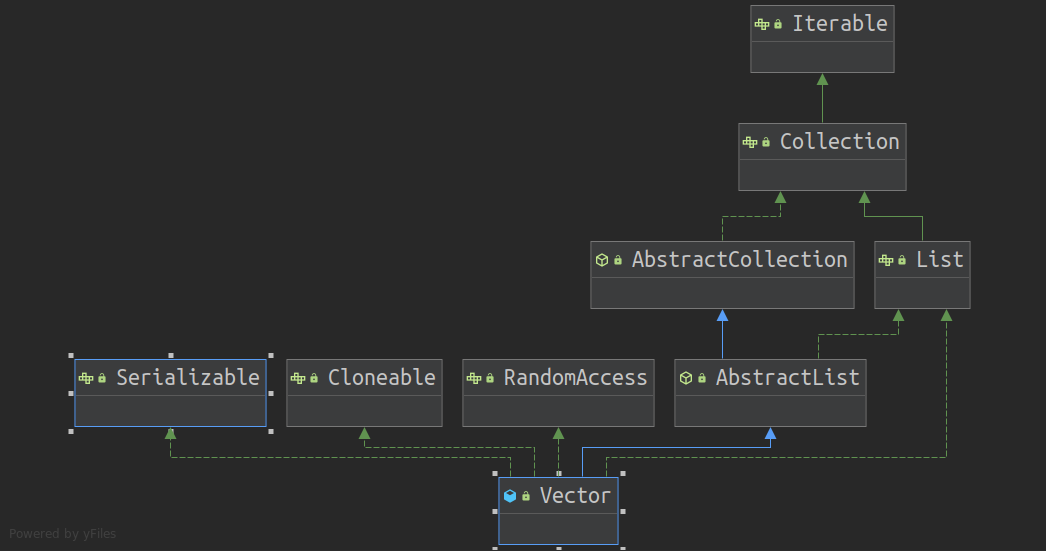
- 支持泛型, 继承了AbstractList类, 实现了List接口
- RandomAccess用来表明其支持随机访问
- Cloneable用来表明其支持拷贝
- Serializable用来表明支持序列化
Vector的实现和ArrayLis基本类似, 底层使用的都是Object类型的数组, 只不过Vector在方法上添加了关键字synchronized, 实现了线程安全.
所以具体的实现就不一一展开来了, 但是其扩容机制大小和ArrayList的不容,其他的部分, 分析Stack源码的时候相关涉及会再分析下
构造函数
Vector()
// 无参构造
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
Vector(int initialCapacity)
// 指定初始化容量
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
// 即指定初始化容量又指定扩容大小
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
Vector(Collection<? extends E> c)
// 构造包含指定collection元素的Vector
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
扩容机制
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
可以看到其扩容机制和ArrayList的不同, ArrayList的扩容是原容量的1.5倍, 但是Vector的扩容机制和capacityIncrement相关
- capacityIncrement>0 则 扩容容量为
capacityIncrement, 最后的容量为oldCapacity + capacityIncrement - capacityIncrement<0 则 扩容容量为
oldCapacity, 最后的容量为2倍oldCapacity
总结
共四个构造函数, 默认的初始化数组容量为10, 扩容大小不是程序内部实现, 而是用户定义, 默认为原数组的两倍, 若是用户指定了扩容大小, 则扩容为指定的容量
Stack源码解读
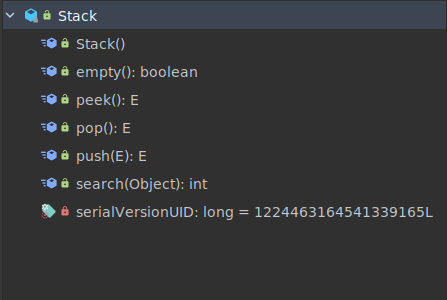
empty()
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
peek()
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
peek()函数调用了父类Vector的 elementAt()方法
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
elementData()函数和ArrayList中的一样
说白了就是返回数组中最后一位的元素
pop()
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
pop()函数调用了父类Vector的 removeElementAt()方法 这个方法和ArrayList的remove(int index)是一样的, 只不过添加了synchronized关键字实现线程安全
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
移除最后一个元素, 基本上不会执行前面的判断分支, 会直接执行
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
push()
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
push()调用了addElement()方法, 该方法首先会确定elementCount是否大于现在数组的容量大小, 若大扩容, 否则直接添加
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
然后在数组尾部添加元素.
search()
返回对应元素所在堆的位置
这个对于底层的数组而言, 是相反的, 所以从尾到头遍历元素,同时因为允许元素为空, 所以首先会先判断查询元素是否为空
感觉这些索引位置和数组第几个元素的问题很恼火, 两者始终差个1
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
// 逆序返回
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
// elementCount记录为数组中的元素个数
// 但是数组是从位置0开始
// 所以在数组中最后一个元素的位置为elementCount-1
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
总结
Vector和ArrayList的异同:
异:
- Vector通过在涉及到线程不安全的方法上添加synchronized关键字实现了线程安全,而ArrayList为线程不安全
- Vector的扩容机制可由用户自定义, 若为定义则扩为原数组的两倍
- ArrayList的扩容机制不能通过用户自定义, 正常情况扩容为原数组的1.5倍
同:
- 底层都是Object数组
- remove方法都不会改变底层数组的大小
Stack
继承Vector类, 所有是线程安全的, 同时底层也是Object数组, 入栈等同于在数组中依次添加元素, 出栈在数组中就是删除数组中最后的元素, 然后将最后的位置设置为空, 数组整体的大小是不会随着出栈而改变的.